MECHANICAL FUNDA
Monday, 3 September 2012
Tuesday, 12 June 2012
1. Basic concepts
Thermodynamics :-
Thermodynamics deals with the transfer of energy of all kinds from one form to another.It is based on first and second law of thermodynamics.There is no mathematical proof of the laws .Their validity depends on general observation of natural phenomenon.
Example like refrigerator, air conditioner, water cooler
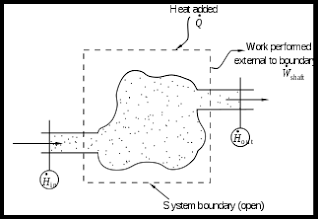
Thermodynamics systems :-
Whenever a change to be analysed it is essential to specify the region in which the change take place.This is done by drawing a boundary around the region .This boundary may be real or imaginary. Everything within the boundary is called system while the region outside the boundary is called surroundings.The of mass and energy between the system and surroundings take place at the boundary.
- closed system
- open system
- isolated system
1. closed system :-
If the mass within the boundary of system does not change , it is called a closed system.
Example like piston cylinder assembly ,
Ignition system ,
Motor car battery,
pressure cooker
2. open system :-
If both mass and energy cross the boundary of a system, it is called a open system.
Example like Boiler ,
hydraulic turbine wheel ,
Motor car engine.
3. Isolated system :-
If neither mass nor energy cross the boundary of a system, it is called a closed system.
Example like Thermos flask.
Homogeneous system:-
A system consisting of a single phase is called a homogeneous system.
Example like water and sugar,
solution of ammonia in water .
Heterogeneous system:-
A system consisting of more than one phase is called a heterogeneous system.
Example like water and steam ,
water and oil.
Mechanical engineering related topics name
- Basic concepts
- Working fluids
- First law and second law of thermodynamics
- Internal combustion engines
- Gas turbine plant
- Steam power plant
- Refrigeration and Air conditioning
- Manufacturing processes
- Power transmission
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)